Drupal, one of the most powerful open-source content management systems (CMS), continues to evolve to meet the growing demands of web development. As we move into 2025, new trends are emerging that are set to shape the future of Drupal, making it more efficient, secure, and user-friendly. Here’s a look at some of the key trends in Drupal development. 1. Drupal 10 Adoption and EnhancementsWith Drupal 10 now widely adopted, organizations are leveraging its latest features, including Symfony 6, CKEditor 5, and improved decoupled architecture. Developers are increasingly upgrading from Drupal 9 to take advantage of better performance, security, and development flexibility. 2. Headless and Decoupled DrupalHeadless CMS architectures continue to gain traction, and Drupal is at the forefront of this movement. By leveraging RESTful APIs, GraphQL, and JSON:API, developers can build robust front-end experiences using frameworks like React, Vue.js, and Next.js while keeping Drupal as the backend. 3. AI and Machine Learning IntegrationArtificial intelligence is making its way into Drupal-based websites. AI-powered chatbots, content personalization, and recommendation engines are becoming standard features, enhancing user engagement and automation within Drupal applications. 4. Increased Focus on Security and ComplianceWith rising cybersecurity threats, Drupal developers are prioritizing security enhancements. Drupal 10 introduces better encryption, improved authentication methods, and compliance-ready features for GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations to ensure data protection. 5. Enhanced Accessibility and InclusivityDrupal has always championed web accessibility, and the latest trends continue to reinforce this. Drupal 10 includes built-in tools for WCAG 2.1 compliance, ensuring websites are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. 6. Drupal as a Digital Experience Platform (DXP)Drupal is transitioning from a traditional CMS to a full-fledged Digital Experience Platform (DXP). With better content workflows, personalization, and integrations with marketing automation tools, businesses can deliver seamless digital experiences across multiple channels. 7. Performance Optimization and Core Web VitalsPerformance is critical for SEO and user experience. Developers are focusing on improving Drupal’s caching mechanisms, optimizing lazy loading, and ensuring compliance with Google’s Core Web Vitals for better search rankings. 8. Cloud-Native Drupal and Serverless HostingMore organizations are adopting cloud-native solutions for Drupal hosting. Platforms like Pantheon, Acquia, and AWS offer scalable and containerized environments, reducing hosting complexities and improving deployment workflows. 9. No-Code/Low-Code Development with DrupalThe rise of low-code and no-code solutions has led to the development of modules that allow non-technical users to build and manage websites more easily. Tools like Layout Builder and Drupal's new Site Studio are making site-building more intuitive. 10. Integration with Emerging TechnologiesDrupal is increasingly integrating with technologies such as blockchain for security, IoT for connected experiences, and augmented reality (AR) for immersive content. These integrations are expanding Drupal’s capabilities beyond traditional web development. ConclusionDrupal’s future looks promising, with continuous innovation making it a preferred choice for enterprises, governments, and developers. Whether it’s through AI-driven automation, improved security, or enhanced front-end experiences, Drupal remains a powerful platform for building the websites and applications of tomorrow. As we look ahead, staying updated with these trends will be crucial for developers and businesses looking to maximize Drupal’s potential. Are you ready to embrace the future of Drupal? |
||
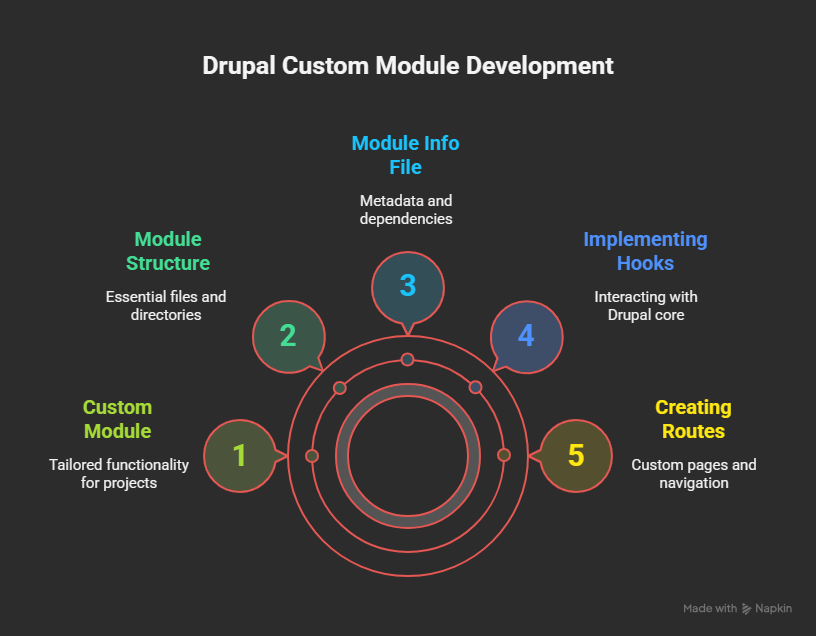
Drupal is a powerful and flexible content management system (CMS) that allows developers to extend its functionality through custom modules. Creating a custom module in Drupal enables you to tailor the CMS to meet specific project requirements. This guide will walk you through the process of developing a custom module in Drupal from scratch.
Understanding Drupal ModulesDrupal modules are PHP-based components that extend the platform's core functionality. There are three types of modules in Drupal:
Steps to Create a Custom Module
1. Setting Up the Module StructureCreate a new directory for your module in Inside the folder, create the following essential files:
2. Defining the Module Info FileCreate the
3. Implementing HooksDrupal uses hooks to allow modules to interact with the core system. The
4. Creating Routes (Optional)If your module requires custom pages, define routes in
5. Enabling the ModuleEnable your module via Drush or the Drupal admin panel:
or navigate to Extend in the Drupal admin UI and enable the module manually. 6. Debugging and Extending
ConclusionCreating custom modules in Drupal allows for flexibility and scalability in development. By following these steps, you can build powerful extensions tailored to your project's needs. Happy coding! |
||